X6 是 AntV 旗下的图编辑引擎,提供了一系列开箱即用的交互组件和简单易用的节点定制能力,方便我们快速搭建流程图、DAG 图、ER 图等图应用。
本文适用于有一定 antv/x6 使用基础的开发者。
实现效果
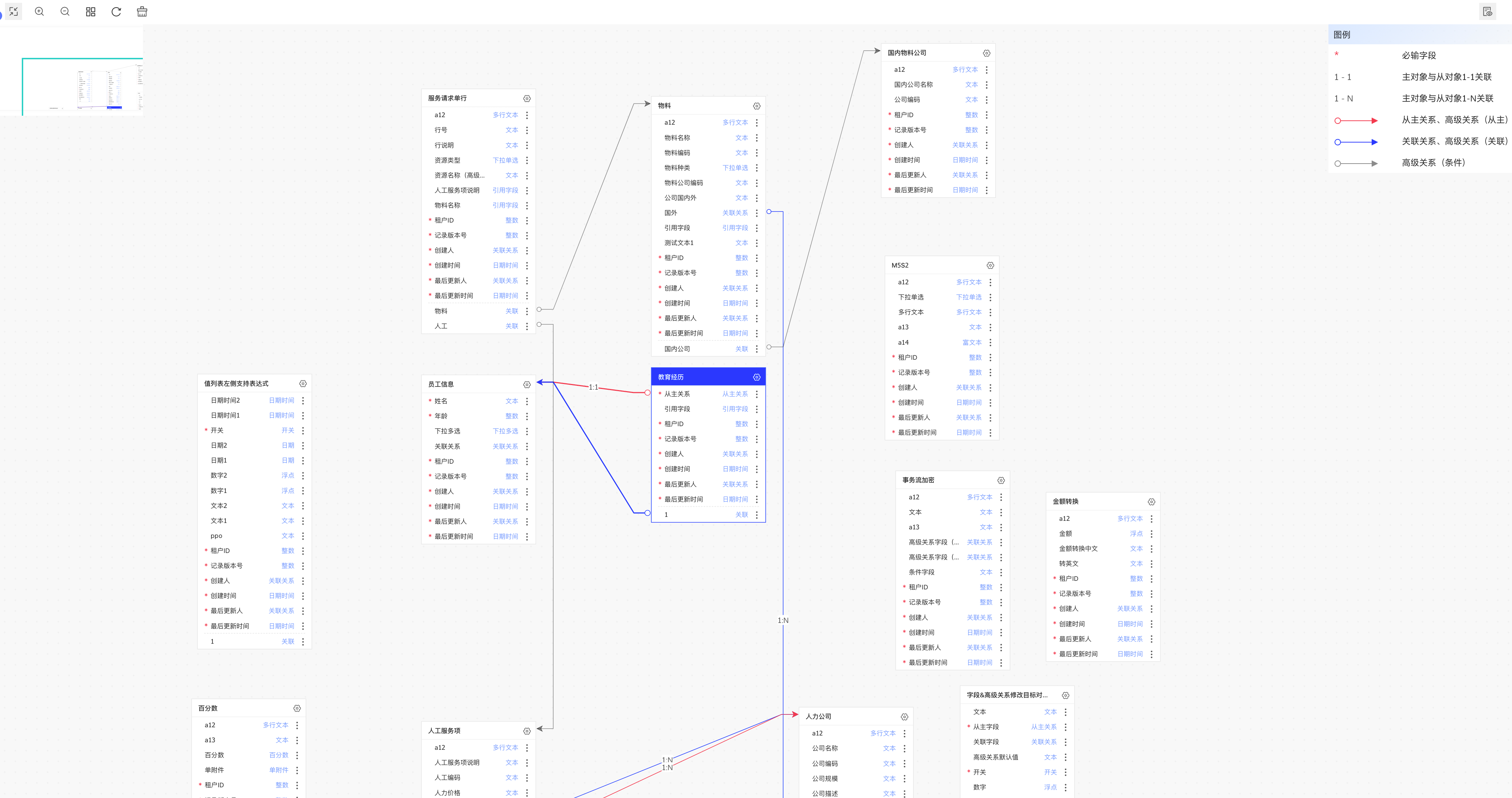
实现效果示意图
业务对象 ER 图用来表示不同领域下不同业务对象之间的关系,如上图所示:
- 一张卡片代表一个节点(业务对象),每个节点下有多个字段。
- 节点间关系,使用带有向箭头的边表示。不同关系会有不同的边颜色对应展示。
- 点击选中某个节点,与该节点所关联的边都会加粗高亮。
- 存在操作按钮,可动态切换每个节点内展示的关联/非关联字段。
- 可通过按钮操作业务对象的增删改查。
- 可拖拽节点,但是不能自建连线。
- 自动布局。
技术栈
- react V16
- mobx V4
- @antv/x6 V1
- @antv/x6-react-shape v1
初始化 Graph
const graph = new Graph({
container: document.getElementById(CONTAINER_ID)!,
width: wrapperRef.current?.clientWidth || 0,
height: wrapperRef.current?.clientHeight || 0,
grid: {
visible: true,
size: 20,
args: {
color: '#f0f0f0',
thickness: 3,
},
},
background: { color: '#f8f8f8' },
interacting: {
nodeMovable: true, // 仅允许节点移动
},
scroller: {
enabled: true,
className: styles['graph-scroller'],
pannable: {
enabled: true,
eventTypes: ['leftMouseDown'],
},
autoResize: true,
},
minimap: {
enabled: true, // 开启缩略图
container: document.getElementById(MINI_MAP_ID)!,
width: 205,
height: 128,
padding: 0,
},
mousewheel: {
enabled: true,
modifiers: ['ctrl', 'meta'],
}, // 允许鼠标滚轮缩放画布
connecting: {
router: {
name: ER_ROUTER, // 基于 er 路由修改后的自定义路由
args: {
direction: 'H',
},
},
// 屏蔽一些主动连线操作
allowEdge: false,
allowPort: false,
allowBlank: false,
allowLoop: false,
allowMulti: false,
allowNode: false,
},
});
在以上的 ER 图的 Graph 配置仅供参考,可根据实际需要调整。全部的配置项可参考官网 Graph。
注册节点

由上图实现效果可以看出,每个节点有样式以及包含部分按钮交互效果,使用 x6 默认的描述 svg 标签的 markup、attrs 等参数实现较为复杂。因此我们采用自定义 react 节点的形式,去创建节点。
注册 React 节点方式如下:
使用 Graph.registerReactComponent(...) 方法将 React 组件或返回 React 组件的函数注册到系统中。
import React from 'react';
import { Graph } from '@antv/x6';
/**
* 注册 ER 图节点
*/
export function registerReactERNode() {
Graph.registerReactComponent(REACT_ER_NODE, <ERNode />);
return () => Graph.unregisterReactComponent(REACT_ER_NODE);
}
<ERNode /> 为 ER 图中每个节点的 react 组件。
使用方式如下:
在初始化画布的 useEffect 中,在调用 new Graph 之前,调用 registerReactERNode 方法。registerReactERNode 会返回一个销毁的方法,在 useEffect 的 return 方法中调用。
useEffect(() => {
// 注册 react ER 图节点
const erReactNodeDispose = registerReactERNode();
// ......
// 仅做初始化布局
const graph = new Graph({......})
return () => {
graph.dispose();
erReactNodeDispose();
// ......
};
}, []);
注册路由
因为 x6 自带的 er 路由没有完全满足场景,所以我们需要在官方提供的 er 路由上做一下参数的修改。 使用官方为注册自定义路由提供的 registerRouter 方法。标准的官方 er 路由实现需要从 x6 的 github 源码中复制出来。

未优化前 优化后
如上图所示,针对节点自身的字段指向自己这种情况做优化。
/**
* 注册 ER 路由
*/
export function registerERRouter() {
Graph.registerRouter(ER_ROUTER, (vertices, options, edgeView) => {
const offsetRaw = options.offset || 32;
const min = options.min == null ? 16 : options.min;
let offset = 0;
let { direction } = options;
const { sourceBBox, targetBBox } = edgeView;
const sourcePoint = sourceBBox.getCenter();
const targetPoint = targetBBox.getCenter();
if (typeof offsetRaw === 'number') {
offset = offsetRaw;
}
if (direction == null) {
let dx = targetBBox.left - sourceBBox.right;
let dy = targetBBox.top - sourceBBox.bottom;
if (dx >= 0 && dy >= 0) {
direction = dx >= dy ? 'L' : 'T';
} else if (dx <= 0 && dy >= 0) {
dx = sourceBBox.left - targetBBox.right;
if (dx >= 0) {
direction = dx >= dy ? 'R' : 'T';
} else {
direction = 'T';
}
} else if (dx >= 0 && dy <= 0) {
dy = sourceBBox.top - targetBBox.bottom;
if (dy >= 0) {
direction = dx >= dy ? 'L' : 'B';
} else {
direction = 'L';
}
} else {
dx = sourceBBox.left - targetBBox.right;
dy = sourceBBox.top - targetBBox.bottom;
if (dx >= 0 && dy >= 0) {
direction = dx >= dy ? 'R' : 'B';
} else if (dx <= 0 && dy >= 0) {
direction = 'B';
} else if (dx >= 0 && dy <= 0) {
direction = 'R';
} else {
direction = Math.abs(dx) > Math.abs(dy) ? 'R' : 'B';
}
}
}
if (direction === 'H') {
direction = targetPoint.x - sourcePoint.x >= 0 ? 'L' : 'R';
} else if (direction === 'V') {
direction = targetPoint.y - sourcePoint.y >= 0 ? 'T' : 'B';
}
if (offsetRaw === 'center') {
if (direction === 'L') {
offset = (targetBBox.left - sourceBBox.right) / 2;
} else if (direction === 'R') {
offset = (sourceBBox.left - targetBBox.right) / 2;
} else if (direction === 'T') {
offset = (targetBBox.top - sourceBBox.bottom) / 2;
} else if (direction === 'B') {
offset = (sourceBBox.top - targetBBox.bottom) / 2;
}
}
let coord: 'x' | 'y';
let dim: 'width' | 'height';
let factor;
const horizontal = direction === 'L' || direction === 'R';
if (horizontal) {
if (targetPoint.y === sourcePoint.y) {
return [...vertices];
}
factor = direction === 'L' ? 1 : -1;
coord = 'x';
dim = 'width';
} else {
if (targetPoint.x === sourcePoint.x) {
return [...vertices];
}
factor = direction === 'T' ? 1 : -1;
coord = 'y';
dim = 'height';
}
const source = sourcePoint.clone();
const target = targetPoint.clone();
source[coord] += factor * (sourceBBox[dim] / 2 + offset);
target[coord] -= factor * (targetBBox[dim] / 2 + offset);
if (horizontal) {
const sourceX = source.x;
const targetX = target.x;
const sourceDelta = sourceBBox.width / 2 + min;
const targetDelta = targetBBox.width / 2 + min;
if (targetPoint.x > sourcePoint.x) {
if (targetX <= sourceX) {
source.x = Math.max(targetX, sourcePoint.x + sourceDelta);
target.x = Math.min(sourceX, targetPoint.x - targetDelta);
}
} else if (targetX >= sourceX) {
source.x = Math.min(targetX, sourcePoint.x - sourceDelta);
target.x = Math.max(sourceX, targetPoint.x + targetDelta);
}
} else {
const sourceY = source.y;
const targetY = target.y;
const sourceDelta = sourceBBox.height / 2 + min;
const targetDelta = targetBBox.height / 2 + min;
if (targetPoint.y > sourcePoint.y) {
if (targetY <= sourceY) {
source.y = Math.max(targetY, sourcePoint.y + sourceDelta);
target.y = Math.min(sourceY, targetPoint.y - targetDelta);
}
} else if (targetY >= sourceY) {
source.y = Math.min(targetY, sourcePoint.y - sourceDelta);
target.y = Math.max(sourceY, targetPoint.y + targetDelta);
}
}
// 如果是自己连自己
if (sourcePoint.x === targetPoint.x) {
target.x = source.x;
}
return [source.toJSON(), ...vertices, target.toJSON()];
});
return () => Graph.unregisterRouter(ER_ROUTER);
}
注册路由方式如下:
在初始化画布的 useEffect 中,在调用 new Graph 之前,调用 registerERRouter 方法。registerERRouter 会返回一个销毁的方法,在 useEffect 的 return 方法中调用。
例:
useEffect(() => {
// 注册 ER 路由
const erRouteDispose = registerERRouter();
// ......
// 仅做初始化布局
const graph = new Graph({......})
return () => {
graph.dispose();
erRouteDispose();
// ......
};
}, []);
ERNode 组件实现


<ERNode/>示例代码如下:
import React, { memo } from "react";
import { ReactShape } from "@antv/x6-react-shape";
import { isEqual } from "lodash";
interface Props {
node?: ReactShape;
}
const ERNode: React.FC<Props> = ({ node }) => {
// 获取节点数据
const data = node?.getData() as BusinessObject & NodeExtraProps;
const {
selectedNodeId,
domainCode,
// ......
} = data;
// 更新节点方法示例
const handleShowNonRelationalFields = () => {
node?.setData({
...node?.getData(),
isShowNonRelationalFields: !isShowNonRelationalFields,
});
};
return // ......
};
export default memo(ERNode, (prev, next) => {
// 精确控制节点渲染
return !isEqual(prev.node?.getData(), next.node?.getData());
});
与普通的 React 组件更新方式不同,ERNode 组件接收一个 node 属性,该属性为 x6 节点实例。node 节点下有个 data 属性。与节点/边关联的业务数据。例如,我们在实际使用时通常会将某些业务数据存在节点/边的 data 上。使用 node.getData() 方法可以获取到节点/边的 data。
为了精确控制 ERNode 组件渲染,避免节点过多时触发无效渲染影响组件性能,我们可以通过监听 node 上 data 的变化,来更新节点的渲染。
如果想要主动触发节点的更新,可以通过调用 node.setData(...) 方法来实现。
如果想要在 ERNode 组件内获取外部 React Context(包括项目中常用的 mobx store) 的值,x6 文档中提供了 Portal 机制。但是使用了该方法获取外部上下文会导致小地图组件无法渲染。因此小地图和 X6ReactPortalProvider 只能二选一。
值得注意的是,HTML/React/Vue 节点内容都是渲染在 SVG 的 foreignObject 元素内部,因为浏览器的兼容性问题,经常会出现一些异常的渲染行为。主要表现形式为节点内容展示不全或者节点内容闪烁。可以通过以下方式来规避:
节点内部元素的 css 样式中不要使用 position:absolute、position:relative、transform、opacity。
在 Safari 浏览器上兼容性表现会更加差。如果项目需要兼容 Safari 浏览器,建议不要在组件中使用 react 组件库(antd、c7n 等)的复杂组件。如果使用了,需要去 Safari 浏览器验证一下是否兼容。
连接桩的实现
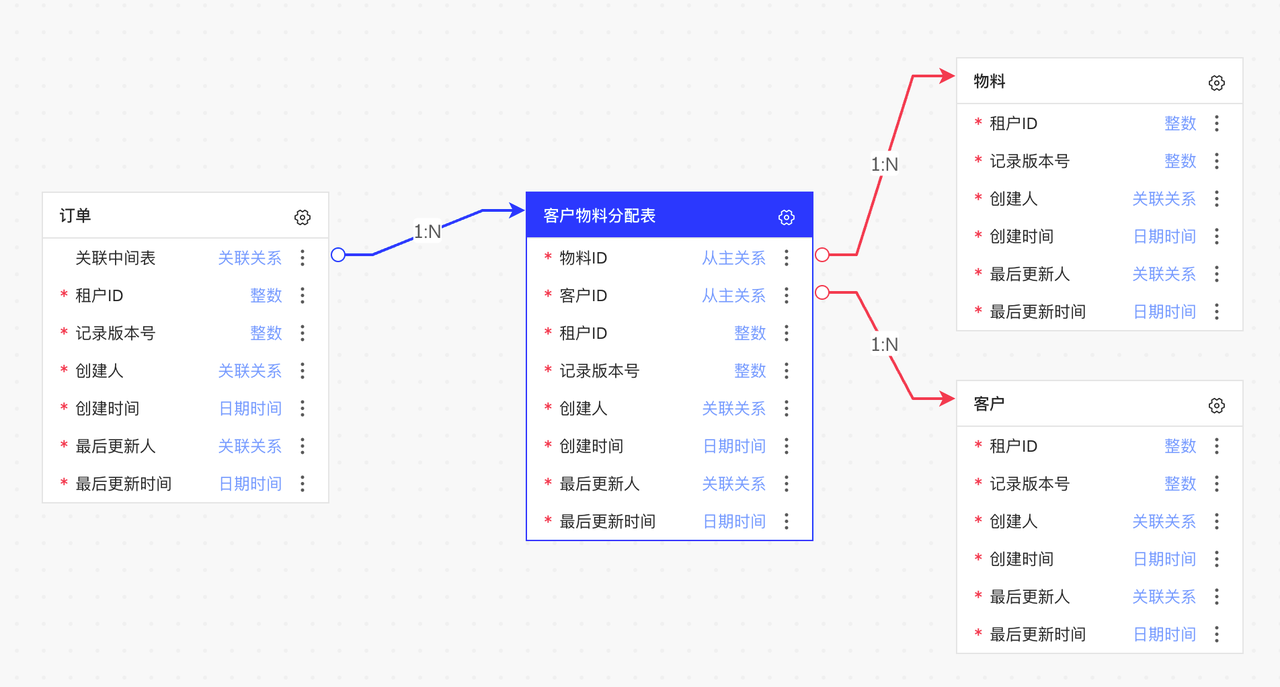
如上图所示,节点与节点间存在连线关系。根据 x6 对边连接位置的要求,我们需要在节点上定义连接桩。根据连接桩的位置,精准连线。
因为连接桩的位置数据和字段类型数据有关联,所以在生成初始化节点数据的时候注入连接桩数据。每个连接桩的形状为字段行的形状,层级 z-index 设置为 -1,隐藏在节点层级之后。

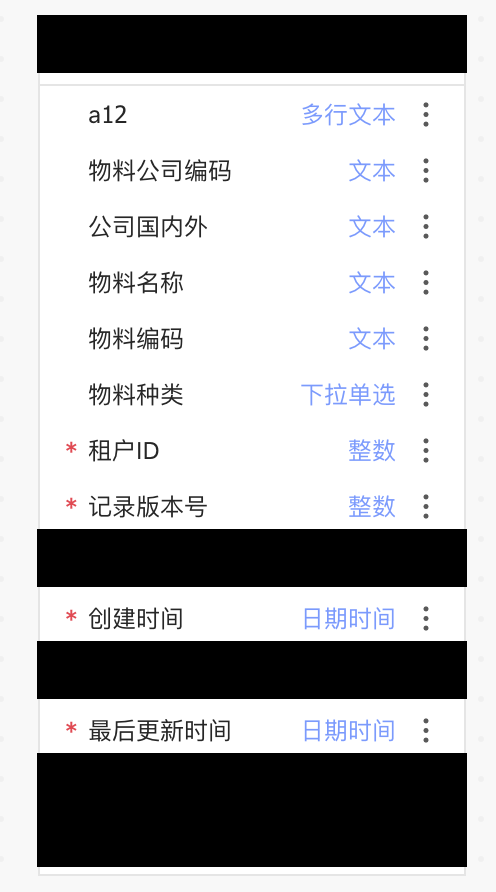
黑色区域即为生成的连接桩区域。连接桩生成的参数可参考如下代码:
const generatePorts = (id: string, attrs: Record<string, any>) => {
return {
id,
markup: [
{
tagName: 'rect',
selector: 'portBody',
},
],
args: {
position: 'top',
},
attrs: {
portBody: {
width: ER_NODE_WIDTH,
strokeWidth: 1,
stroke: 'rgba(0,0,0,0)',
fill: 'rgba(0,0,0,0)',
magnet: true,
transform: 'matrix(1,0,0,1,0,0)',
...attrs,
},
},
zIndex: -1,
};
};
attrs 为额外属性,在列表数据遍历时动态注入。
// 设置连接桩
const ports: any[] = [];
// 设置标题连接桩
ports.push(
generatePorts(item.businessObjectId, {
height: ER_LINE_HEIGHT,
})
);
// 设置业务对象字段连接桩
item.businessObjectFields.forEach((field, index) => {
// 如果是关联类型
if (RELATION_TYPE.includes(field.componentType)) {
ports.push(
generatePorts(field.businessObjectFieldId, {
height: ER_LINE_HEIGHT,
refY: ER_TITLE_HEIGHT + ER_LINE_HEIGHT * index,
})
);
}
});
根据不同的列表 y 轴位置结合索引生成 refY 参数,使得连接桩矩形在 y 轴产生偏移定义到所对应的关联字段区域。
ERNode 节点中有个隐藏/显示非关系字段的功能,该功能会影响到连接桩的生成。我们通过在 node 的 data 数据上绑定 isShowNonRelationalFields 属性来控制是否显示非关系字段。每当值切换时,连接桩位置也得重新计算。
节点和边数据的生成
在初始化节点的时候我们需要把后端传过来的数据格式化成 x6 节点需要的数据格式。
- 后端的数据
- 格式化后的 x6 数据
enum SourceType {
PREDEFINE = 'PREDEFINE', // 系统预置
PLATFORM = 'PLATFORM', // 平台自定义
TENANT = 'TENANT', // 租户自定义
}
// 业务对象字段数据(包含关联)
interface BusinessObjectField {
businessObjectFieldId: string;
businessObjectId: string;
businessObjectFieldCode: string;
businessObjectFieldName: string;
requiredFlag: boolean;
componentType: FieldComponentType; // 业务对象组件类型
inheritSourceType: string;
requiredFlagValue: string;
masterBusinessObjectId?: string; // 关联的业务对象id
linkRelationType?: string; // 连接类型 ONE_TO_ONE ONE_TO_MANY
relateType?: string; // 关系类型
}
// 业务对象高级关联数据
interface BusinessObjectAssociate {
_token: string;
businessObjectAssociateId: string;
associateName: string;
associateType: string;
associateCode: string;
linkRelationType: string;
associateBusinessObjectId: string;
preConditionFlag: boolean;
}
// 业务对象数据
interface BusinessObject {
_token: string;
businessObjectId: string;
businessObjectCode: string;
businessObjectName: string;
domainId: string;
domainCode: string;
publishStatus: string;
businessObjectFields: BusinessObjectField[];
skipResetPhysicalSyncFlag: boolean;
extendFieldCreatedFlag: boolean;
updatePhysicalFlag: boolean;
sourceType: SourceType;
businessObjectCategory: string;
flexFieldEnabledFlag: boolean;
extendTableEnabledFlag: boolean;
objectVersionNumber: number;
businessObjectAssociateList?: BusinessObjectAssociate[];
relationBusinessObjectIds?: string[]; // 与此对象关联的业务对象id
extendFieldPrefixRule?: string;
physicalModelType?: string;
}
// 连接桩数据
interface Port {
id: string;
markup: any[];
args: {
position: string;
};
attrs: {
portBody: {
width: number;
strokeWidth: number;
stroke: string;
fill: string;
magnet: boolean;
transform: string;
height: number;
refY?: number;
};
};
zIndex: number;
}
// x6 节点数据
interface Node {
id: string;
component: string;
data: object; // 渲染 ERNode 组件所需的数据
height: number;
width: number;
shape: string; // 区分节点或边
ports: Port[];
}
// x6 边数据
interface Edge {
attrs: any[];
labels: any[];
shape: string;
source: {
cell: string;
port: string;
};
target: {
cell: string;
port: string;
};
}
type GraphData = Node[] | Edge[];
通过 formatBoDataToReactERGraph 方法(见项目代码)去格式化后端数据,该方法会返回一个符合x6渲染数据类型的数组,数组中的每一项都是一个节点或边的数据。
后端返回的边数据包含全部与此节点有关联的数据。但是页面上展示的节点并不全是与此节点有关联的,所以我们在方法的最后一步需要对边数据进行过滤,只保留与画布上节点有关联的数据。如果添加的边数据的指向 id 的节点没有在画布中,则会报错。
生成边的代码如下:
// 设置普通字段箭头
item.businessObjectFields.forEach((field) => {
if (field.linkRelationType) {
const edge: any = {
shape: 'edge',
source: {
cell: item.businessObjectId,
port: field.businessObjectFieldId,
},
target: {
cell: field.masterBusinessObjectId,
port: field.masterBusinessObjectId,
},
attrs: {
line: getEdgeLine(field.componentType),
},
labels: getEdgeLabels(field.linkRelationType),
};
edgesData.push(edge);
}
});
边的起终点数据都需要 cell 和 port 属性来决定边的坐标。
cell代表是目标节点,取自businessObjectFieldId。port代表是当前节点中的哪个连接桩,取自businessObjectId。
选中节点高亮周围边功能

每个 ER 节点分为选中和非选中两种状态。当节点为选中状态时,会高亮节点和与节点相连的边。
判断画布中哪个节点被选中的数据存在于节点的 data 数据中,通过 selectedNodeId 属性来控制。如果 selectedNodeId 和当前节点的 id 相等,则代表当前节点被选中。
在外部数据管理中,selectedNodeId 存在于 Mobx Store 中统一管理,并且和 x6 画布中的节点数据进行绑定的。当更新 Mobx Store 的 selectedNodeId 的时候,会触发 x6 画布中节点的更新。
我们可以通过 graph 提供的 on 方法,去监听节点点击事件。
function addNodeClickListener({ node }: NodeView.EventArgs['node:click']) {
if (!graph) return;
erStore.setState('selectedNodeId', node.getData()?.businessObjectId || '');
}
// 添加点击事件
graph?.on('node:click', addNodeClickListener);
useEffect(() => {
selectNode();
}, [erStore.getState('selectedNodeId')]);
这样使得副作用逻辑全部被提取到 selectNode 这一个方法中。
export const NORMAL_SOURCE_EDGE_ATTR = {
strokeWidth: 1,
sourceMarker: {
r: 4,
cx: 4,
},
};
export const SELECTED_SOURCE_EDGE_ATTR = {
strokeWidth: 2,
sourceMarker: {
r: 5,
cx: 5,
},
};
const curNodeRef = useRef<Cell>(); // 当前选中的节点
const curEdgesRef = useRef<Edge[]>([]); // 当前选中的边
// 选中一个节点
function selectNode() {
const selectedNode = graph?.getCellById(erStore.getState('selectedNodeId'));
const selectedNodeId = selectedNode?.getData()?.businessObjectId || '';
// 还原上一个选中节点颜色
if (curNodeRef.current) {
curNodeRef.current?.setData({
...curNodeRef.current.getData(),
selectedNodeId,
});
}
// 还原边
if (isArray(curEdgesRef.current) && curEdgesRef.current.length > 0) {
curEdgesRef.current?.forEach((edge) => {
edge.attr('line/strokeWidth', NORMAL_SOURCE_EDGE_ATTR.strokeWidth);
edge.attr('line/sourceMarker', {
...(edge.getAttrs().line.sourceMarker as any),
...NORMAL_SOURCE_EDGE_ATTR.sourceMarker,
});
});
}
if (selectedNode && graph) {
// 设置选中状态
selectedNode.toFront();
selectedNode.setData({
...selectedNode.getData(),
selectedNodeId,
});
// 设置边宽度
const edges = graph.getConnectedEdges(selectedNode);
edges.forEach((edge) => {
edge.attr('line/strokeWidth', SELECTED_SOURCE_EDGE_ATTR.strokeWidth);
edge.attr('line/sourceMarker', {
...(edge.getAttrs().line.sourceMarker as any),
...SELECTED_SOURCE_EDGE_ATTR.sourceMarker,
});
});
curNodeRef.current = selectedNode;
curEdgesRef.current = edges;
} else {
curNodeRef.current = undefined;
curEdgesRef.current = [];
}
}
在每次新选择一个节点时读取上一次存储的节点数据。如果有数据就还原,再设置当前选择节点的数据并备份到 curNodeRef 和 curEdgesRef 中。
自动布局
自动布局方法修改自 @antv/layout 中第三方开发者写的 ErLayout。主要修改了对数据格式的兼容和节点环绕的间距。
以下是 ERLayout 使用方法。
/**
* 执行 ER 布局算法
* @constructor
*/
export function executeERLayout(graph: Graph) {
const nodes = graph.getNodes();
const edges = graph.getEdges();
const width = graph.container.clientWidth;
const height = graph.container.clientHeight;
// 加载 ER 图布局
const ERLayoutInstance = new ERLayout({
nodes,
edges,
nodeMinGap: 20,
width,
height,
});
return new Promise<void>((resolve) => {
ERLayoutInstance.execute().then(({ nodes: newNodes = [] }) => {
nodes.forEach((item) => {
const node = newNodes.find((n) => n.id === item.id);
if (node) {
item.position(node.x || 0, node.y || 0);
}
});
graph.zoomToFit({ padding: 10, maxScale: 1 });
resolve();
});
});
}
位置缓存
如果一个节点被拖动到一个新的位置,那么这个节点的位置信息就会被缓存到 Mobx Store 中。当再次打开这个节点的时候,就会读取缓存的位置信息,然后设置到节点上。
nodePositions 用来存储节点的位置信息,key 为节点的 id(即业务对象id),value 为节点的位置信息。
// 重新设置节点
const nodePositions = erStore.getState('nodePositions', true);
const _cacheNodePositions = cloneDeep(nodePositions);
const cells: any[] = [];
const graphNodeIds = graph.getNodes().map((item) => item.id);
let newNodeId = '';
nodes.forEach((node) => {
if (graphNodeIds.indexOf(node.id) === -1) {
newNodeId = node.id;
}
// 读取缓存位置
const position = nodePositions[node.id];
if (position) {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-param-reassign
node.x = position.x;
// eslint-disable-next-line no-param-reassign
node.y = position.y;
} else {
// 获取当前 graph 平移的位置, 添加节点到画布左上角(如果缩略图在展开,需要避开缩略图位置)
const { x, y } = graph.scroller.widget!.getVisibleArea();
let newX = isShowMiniMap ? x + 200 : x;
let newY = isShowMiniMap ? y + 140 : y;
// 当前画布上存在的节点的位置信息
const curNodePositions = graph.getNodes().map((item) => {
return item.position();
});
const _nodePositions = `${curNodePositions
.map((item: any) => `${item.x},${item.y}`)
.join(';')};`;
while (_nodePositions.indexOf(`${newX},${newY};`) !== -1) {
newX += 20;
newY += 20;
}
// eslint-disable-next-line no-param-reassign
node.x = newX;
// eslint-disable-next-line no-param-reassign
node.y = newY;
// 缓存位置
nodePositions[node.id] = { x: newX, y: newY };
}
cells.push(graph.createNode(node));
});
edges.forEach((edge) => {
if (!graph.getCellById(edge.id)) {
cells.push(graph.createEdge(edge));
}
});
// 把节点和边设置到画布上
graph.resetCells(cells);
// 没有缓存位置时,一次添加多个节点,使用自动布局
if (keys(_cacheNodePositions).length === 0 && ids.length - graphNodes.length > 1) {
await executeERLayout(graph);
}
// 缓存节点位置
graph.getNodes().forEach((node) => {
const { x, y } = node.getBBox();
nodePositions[node.id] = { x, y };
});
erStore.setState('nodePositions', nodePositions);
// 如果是新的节点,放到画布层级最前面
if (newNodeId) {
const newNode = graph.getCellById(newNodeId);
if (newNode) {
newNode.toFront();
}
}
设置节点位置信息在 updateGraphCells 方法中,这里只展示了部分代码。
如果添加的是新的节点且没有缓存位置,则节点会从画布左上角往右下角根据偏移量进行计算位置。
